
 |
| Home | Teacher | Parents | Glossary | About Us | |||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
Area is always a positive number. It represents the number of square units needed to cover a shape, such as a polygon or a circle. We generally use formulas to calculate areas.
Area of: rectangle | square | parallelogram | triangle | trapezoid | circle
Area
of a Rectangle
A rectangle is a good, simple shape to begin with. The area of a rectangle
is equal to the product of the length of its base and the length of its height.
The height is a segment that is perpendicular to the base. For a rectangle,
the base and height are often called the "length" and the "width", and sometimes
the height is referred to as the "altitude."
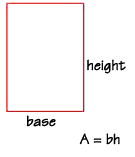
Let's find the area of this rectangle, with a base measuring 4 feet and a height measuring 6 feet. Using the formula, we multiply 4 feet times 6 feet, to get 24 square feet.
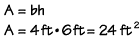
Area
of a Square
A square is a special rectangle, and you can find its area using the rectangle
formula. However, since the base and height are always the same number for
a square, we usually call them "sides." The area of a square is equal to the
length of one side squared.
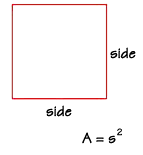
If the length of one side of this square is 4 centimeters, what is the area? We substitute the value "4 cm" into the formula, and we find the area to be 16 square centimeters.
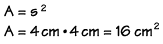
Area
of a Parallelogram
To find the area of a parallelogram, we can use the same formula that we used
for the area of a rectangle, multiplying the length of the base times the
length of the height.
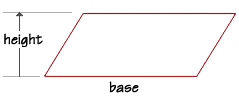
Let's find the area of a parallelogram that has a base of 23 cm and a height of 7 cm. If we substitute the values into the formula, we find that the parallelogram has an area of 161 square centimeters.
![]()
Area
of a Triangle
What about triangles? This sketch of a quadrilateral shows us that one diagonal
separates the interior area into two equal parts.
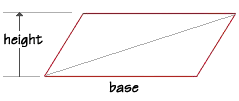
The area of a triangle is therefore one-half the area of the quadrilateral, which is base length multiplied by the height. What is the area of a triangle with a base length of 23 feet and a height of 16 feet? Substitute the values into the formula, and we find the area to be 184 square feet.
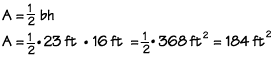
Area
of a Trapezoid
To find the area of a trapezoid, we can draw a diagonal so the trapezoid is
divided into two triangles.
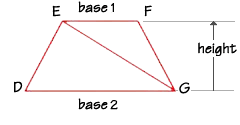
You can see that the area of the trapezoid DEFG is equal to the sum of the area of the two triangles EFG and DEG.
Area
of triangle EFG = ½bh = ½(base1)h
Area of triangle DEG = ½bh = ½(base2)h
Area
of the trapezoid DEFG = ½(base1)h + ½(base2)h. Since the height
of triangle EFG and DEG are the same, we can write the formula for the area
of a trapezoid (either way is correct):
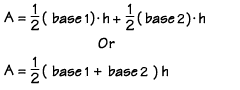
If trapezoid DEFG has a height of 8 inches, base DG measures 12 inches and base EF measures 7 inches, what is the area of the trapezoid? If we substitute the values into the formula, we find the area to be 76 square inches.
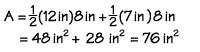
Area
of a Circle
Finally, we'll look at how to find the area of a circle. To help us understand
circle area better, first we'll draw a square, and inscribe a circle in it,
which means to draw the circle inside the square so that the circle just touches
each side of the square.
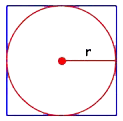
We can find the area of this square by first finding the area of the four smaller squares—each with sides equal to r, the radius of the circle—and adding them together.
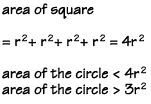
Notice that the sides of the square are twice as long as the radius of the circle. You could also find the area of the square by multiplying the side times the side, or 2r x 2r, which also equals 4r2.
You can see that the area of the circle must be less than the area of four of the squares. But how much less? We could make an educated guess and say that the area of the circle might be a little bit larger than three of the smaller squares.
The actual number
we're looking for, which is between 3 and 4, is the special number called
pi, represented by the Greek letter ![]() .
Pi is approximately equal to 3.14.
.
Pi is approximately equal to 3.14.
![]()
The symbol you see here means "approximately equal to." Pi actually has an unending number of decimal points, but 3.14 is usually close enough for our calculation purposes. Pi is the ratio between the diameter and circumference of a circle.
The final formula for the area of a circle is shown here.
![]()
Let's say your watch face has a diameter of 1 inch, so its radius is ½ or 0.5. We can find its area like this:
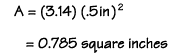
| Homework Help | Geometry | Polygons | |||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||